One of the core principles of system design is governance: The ability to maintain a system of record and demonstrate compliance with external regulations as well as internal policies. In multi-cloud settings governance has become more complex. The most effective way to assure multi-cloud and hybrid cloud compliance is by using a consolidated cloud service catalog.
According to the Cloud Working Group of the Object Management Group (formerly the Cloud Standards Customer Council), six functions are required in a comprehensive cloud management platform (CMP). It’s no coincidence that service management is at the core of all six key cloud features.
First of the six requirements outlined by the group is the ability to integrate with internal and external systems, such as AWS and other public clouds, OpenStack for private clouds, directory services, and other third-party systems. TechTarget’s Robert Sheldon offers 6 key features for multi-cloud management in a recent article and identifies Morpheus as a CMP that provides the ability to integrate source code management and build automation with GitHub, Gradle, Jenkins, Chef, Puppet, and other tools.
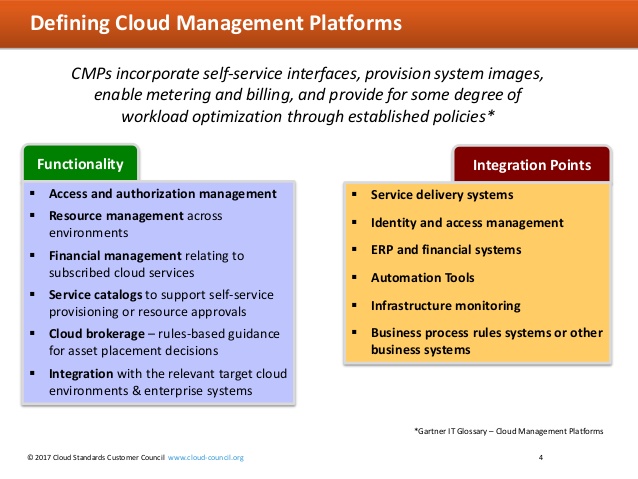
The Cloud Working Group of the Object Management Group identifies six functions and six integration points required in a cloud management platform.
The second of the requirements for a CMP is the use of a centralized portal that supports administration and access to system information, and also user access to a comprehensive cloud service catalog that includes analytics, reporting, and optimization. Requirement #3 is service monitoring and capacity management, while #4 is managing the resources used to deliver cloud resources. Morpheus’s checks these boxes as well’ from initial resource discovery and tagging to consolidated reporting to built-in monitoring, analytics, and backup. The result is more efficient provisioning and de-provisioning of cloud workloads.
Rounding out the Cloud Working Group’s six CMP requirements are governance and security at #5, and financial management at #6. The former necessitates policy-based management of cloud services, including the logic required to track and report on compliance. It also encompasses encryption and identity and access management. Financial management entails metering resource and service usage, cost allocation, chargeback reports for stakeholders, invoicing, and cost forecasting.
Sheldon singles out Morpheus for its stellar financial management capabilities, which deliver insights into public cloud costs and include inline comparison tools. The Intelligent Analytics built into Morpheus help decision makers forecast more accurately and optimize spending.
Cloud service catalogs sit at the intersection of speed and risk
Service reuse, enhanced business agility, and faster time-to-market are among the goals of cloud projects. However, it isn’t always easy to quantify the benefits of specific cloud services to the business. Cloud service catalogs allow an organization to do so by centralizing the discovery and use of the services, and by acting as the system of record and sole gateway to multi-cloud resources for applications and users.
The cloud services comprising the catalog cover application functionality as well as the data required by users and applications. Companies benefit by being able to reuse services across apps, and by allowing services to reside on different public and private cloud platforms. VMware’s Guide to Defining Your Cloud Services Catalog highlights the two key benefits of a service catalog: centralized control, discovery, and access; and effective governance.
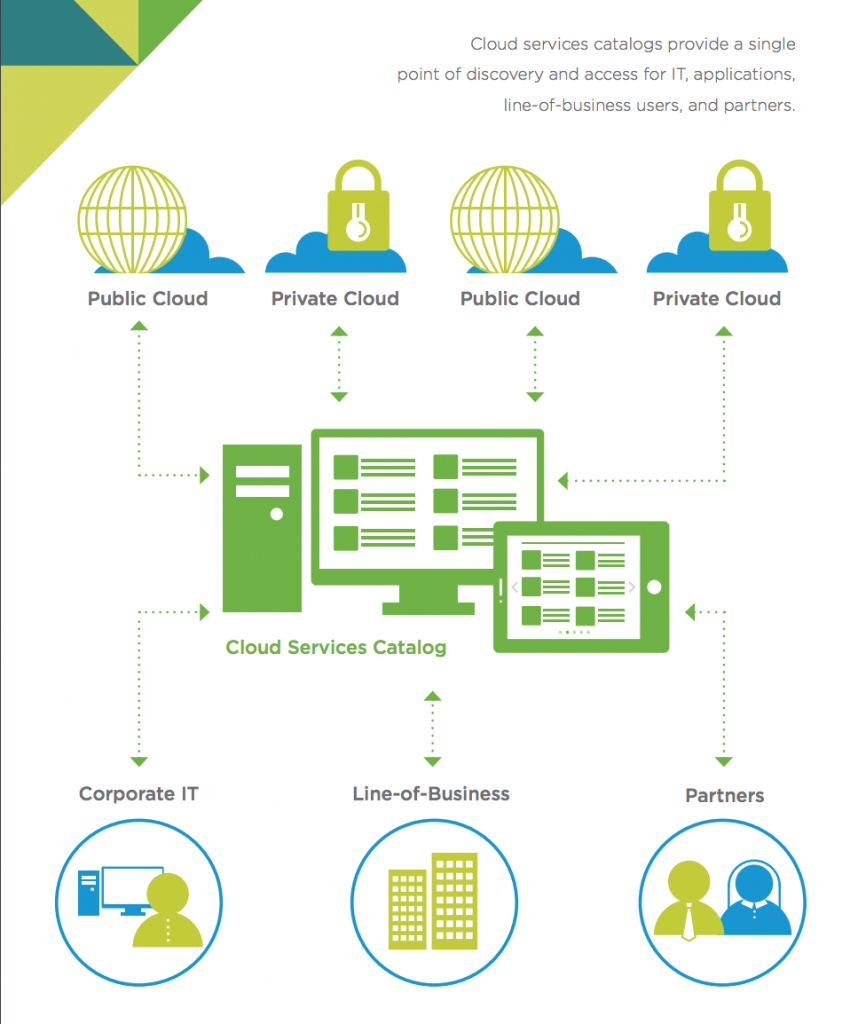
Another important role of the cloud service catalog relates to the need to automate cloud management. Automation removes risk (i.e. people) and is tied directly to effective compliance, security, and best practices. Automated resource management can be extended to shield users and developers from the need to manually conform to policies and procedures. A policy-driven approach to cloud service management allows performance monitoring, troubleshooting, and remediation to be automated across multi-clouds.
Of equal importance is the business side of the cloud-service equation: cost metering and cost accounting. This encompasses charge-back and show-back monitoring as well as analytics to predict future costs. An automated service catalog makes possible an “assembly” approach to application development that saves time and money by encouraging service reuse. The result is faster, more agile DevOps and increased ROI.
Top-notch service support is a big reason TechRadar’s Nate Drake named Morpheus one of the best cloud orchestration platforms for 2018. Drake cites Morpheus’s ability to allow users to build service catalogs and complex multi-cloud structures quickly and simply. In addition to having access to stack visualization tools, users can connect service catalogs to ServiceNow, create policies for workflows, and monitor all configuration management operations.
Morpheus also integrates with DevOps tools for managing source code repositories from GitHub and Git, as well as setting policies for completing service requests, automated cleanup, and pausing services during off-peak times.
Consolidating multi-cloud governance is key to compliance
The proliferation of cloud service environments has led to an explosion in the number of identities used to access cloud resources. Creating roles and management privileges in cloud settings is as challenging as managing existing identity and access controls (IAM), according to Dave Shackleford in a recent TechTarget article. Your cloud service catalog serves as the central repository from which lists of users, groups, roles, and privileges are extracted using cloud-native or third-party tools. The cloud service catalog also does double duty by providing the mechanism for logging and event monitoring for the entire multi-cloud environment.
In a recent interview, IT industry analyst Eric Winton explains the benefits of extending an existing service catalog to cloud platforms. A service catalog is the best way to take advantage of the flexibility of the cloud in choosing and integrating best-of-breed tools from multiple cloud providers. Winton concludes that cloud-based services are quickly supplanting their IT counterparts. Cloud service catalogs will drive the multi-cloud and hybrid cloud infrastructure of the future.
ITSM tools like ServiceNow and Cherwell have become standard operating tools in connecting IT users and developers to resources however they are not explicitly designed for cloud provisioning and application platform deployment. This is one reason Morpheus has built-out integrations for both of these tools. By using Morpheus as the underpinning automation and orchestration platform organizations can update and maintain CMDB records and manage approvals through their ITSM tool of choice.
Let us know if you’d like a demo to learn more!